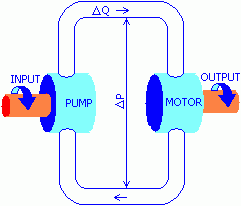
| Principle: Hydrostatic CVTs convert rotational
motion into fluid flow (hydrostatic pump), and then back to rotational
motion (hydrostatic motor).
|
|
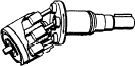
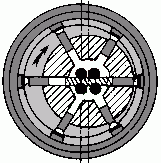
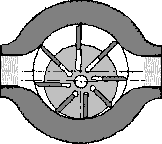
| The most common types of hydrostatic units:
|
|
| Some examples of "Hydrostatic" CVTs: |
|
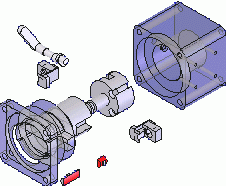 B-Technology |
 Folsom_Technologies |
 Hydristor |
 IHC-Holland |
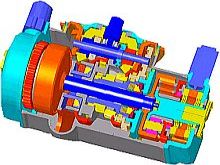 Silvatech |
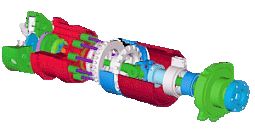 Torvec-IVT |
Hydrostatic CVTs for Tractors: |
|
 Claas'CVT |
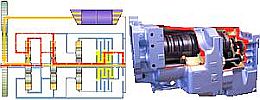 Deutz-Fahr |
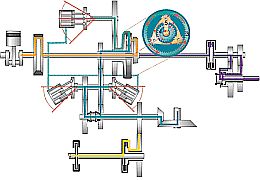 Fendt-Vario-Getriebe |
 John Deere |
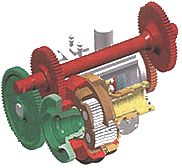 Steyr CVT |
|
Hydrostatic CVTs for Motorcycles: |
|
 Honda Hydramatic |
 Dryvtech 2x2x2 |
Hydrostatic CVTs for Bikes: |
|
 Liquid Drive (PowerEngine) |
|